Skin & Subcutaneous Biopsy
A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue for laboratory examination.
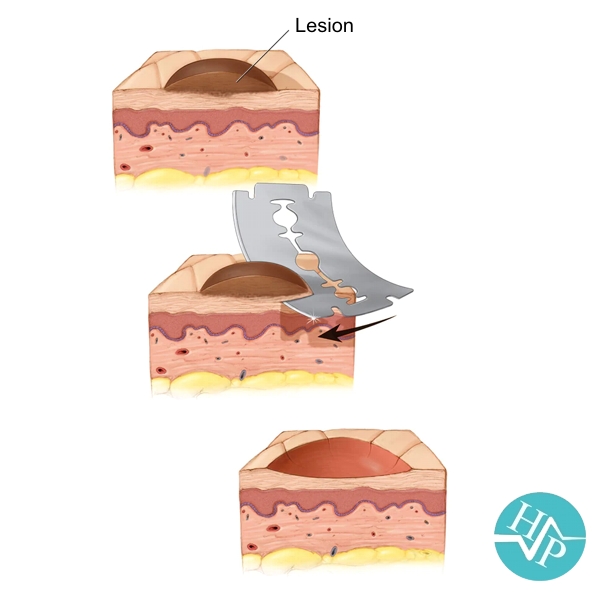
A skin lesion biopsy is when a small amount of skin is removed so it can be examined. The skin is tested to look for skin conditions or diseases. A skin biopsy can help your health care provider diagnose or rule out problems such as skin cancer or psoriasis.
Most procedures can be done in outpatient surgical clinic. There are several ways to do a skin and subcutaneous biopsy. Which procedure you have depends on the location, size, and type of lesion. A lesion is an abnormal area of the skin. This can be a lump, sore, or an area of skin color that is not normal. Before a biopsy, your provider will numb the area of skin so you don't feel anything. The different types of skin biopsies are described below.