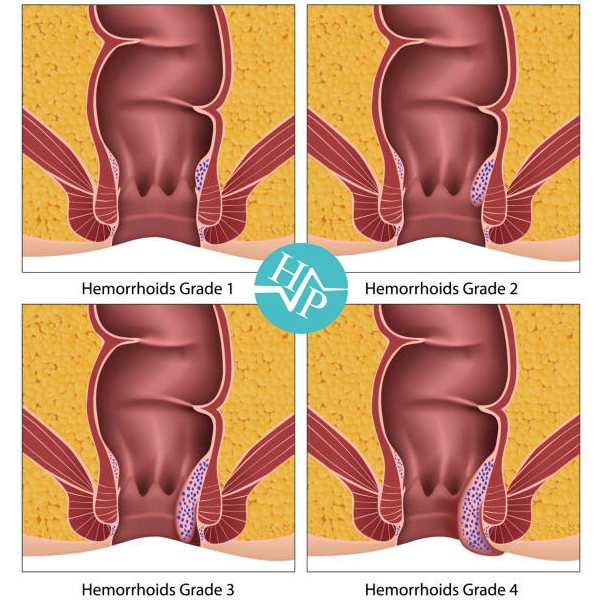
Haemorrhoids
Haemorrhoids are swollen veins in the anus or lower part of the rectum.
Causes
Haemorrhoids are very common. They result from increased pressure on the anus.
This can occur during pregnancy or childbirth, and due to constipation. The
pressure causes the normal anal veins and tissue to swell. This tissue can
bleed, often during bowel movements.
Haemorrhoids may be caused by:
-
Straining during bowel movements
-
Constipation
-
Sitting for long periods of time, especially on the toilet
-
Certain diseases, such as cirrhosis